This course focuses on how to use routing and tool use with LlamaIndex. A real example of building an example of advanced RAG system. The system can route the query based on what’s asked for. Then, also let LLMs use tools, again for necessity.
Router Query Engine
The queries do not have to perform a vector search right away all the time. Some queries may ask for a summary, instead of performing a vector search. For this, LlamaIndex has three index types VectorStoreIndex, SummaryIndex and Knowledge Graph Index. This course covers only the first two.
These indexes are initialized and then passed to t QueryEngineTool1 individually. Finally, a RouterQueryEngine initialized with these tools, along with a selector.
Tool Calling
As discussed in Large Language Models as Tool Makers. This part covers FunctionTool. The class is a helper for converting pure Python functions into LLM-usable functions.
An example of the tool’s usage is similar to LangChain’s Self-Query. Which allows metadata filtering through the query. For example, ”What was the revenue based on the last quarter’s financial report?”. This query, actually asks for only one document, therefore, the system should apply a filter something like {"file_name":"Financial_report_2024_Q1"} the perform the vector search to find the revenue.
Tools like QueryEngineTool can also be used by LLM.
Building and Agent Reasoning Loop
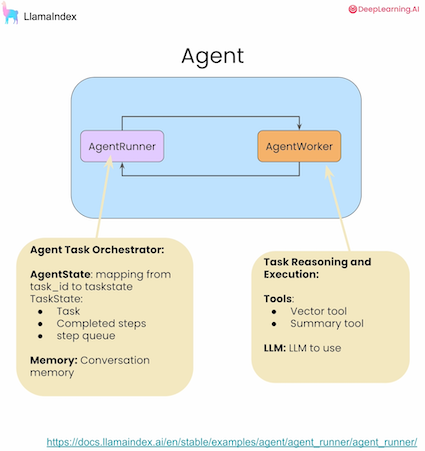
This is where things get advanced. Agents are a complex part of the RAG system and LlamaIndex. Agents are capable of using tools sequentially. Resulting to perform complicated tasks.
Data Agents are LLM-powered knowledge workers in LlamaIndex that can intelligently perform various tasks over your data, in both a “read” and “write” function. They are capable of the following:
- Perform automated search and retrieval over different types of data - unstructured, semi-structured, and structured.
- Calling any external service API in a structured fashion, and processing the response + storing it for later.
Second part of the section focuses on Debuggability and Control of the agents
 Resource: Course Documents
Resource: Course Documents
Building a Multi-Document Agent
This section first covers usage of tools and routings on multiple documents. Then defines a problem: Having multiple tools for multiple documents can blow up the number of tools that the LLMs can select. This may easily cause wrong tool usage. To solve this issue this section suggests to built tool retrieval.
Tool Retrieval
What if there are thousands of documents and at least two (e.g. summaryTool, vectorSearchTool) there will be twice as much tools to select from.2
To overcome this the course suggests building a tool retrieval approach.
- Store tools with a
ObjectIndex. Which allows indexing arbitrary Python objects - Apply vector search on this index to get a list of possible tools
- Let LLM chose from these subsampled list of tools to use for initial query.
 Resource: Course Documents
Resource: Course Documents
Comments